
table 1 001.jpg Molecular geometry, Chemistry, Molecular
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.
Lewis Structure And Molecular Geometry Worksheet —
Molecular Geometry Van Koppen/Offen Procedure: draw Lewis Structure, determine Steric Number (SN), Molecular Geometry and Hybridization SN = # of atoms bonded to the central atom plus # of lone pairs on the central atom (SN = the effective number of electron pairs surrounding a central atom).

VSEPR Theory — Definition & Overview Expii
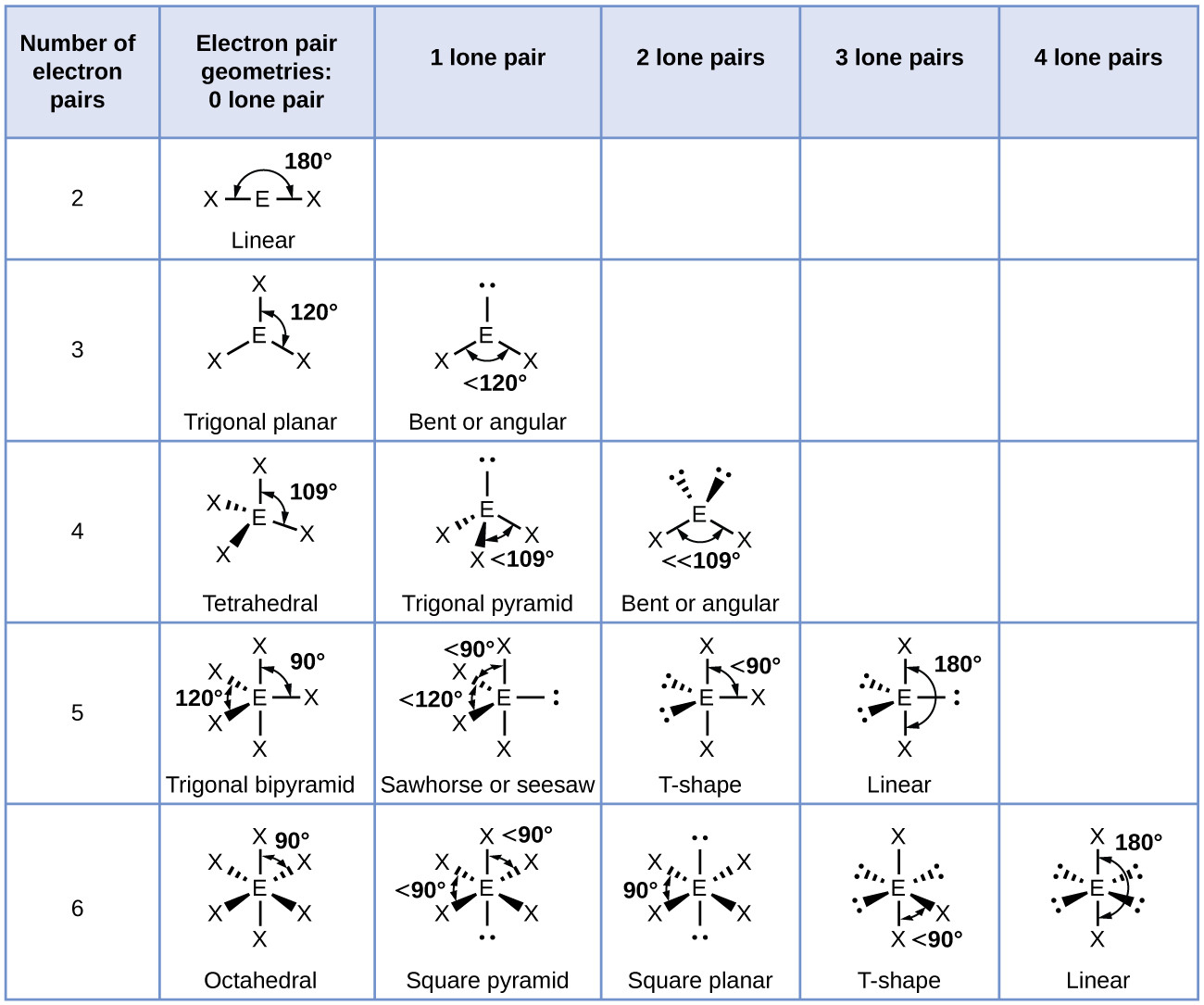
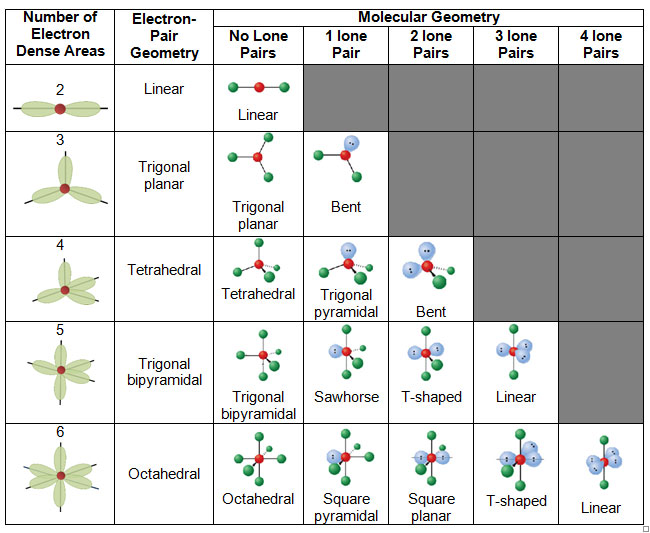
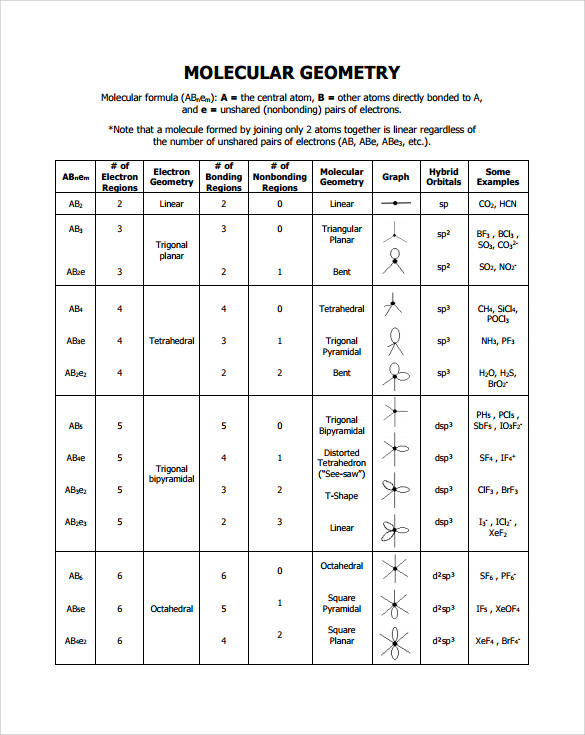
The molecular geometry is bent due to the lone pair of electrons compressing the bond angles to 115.4 o and is represented by AX 2 E. Tetrahedral Electron Pair Geometry and Molecular Shapes. Methane, CH 4, has a tetrahedral electron pair geometry and a tetrahedral molecular geometry, AX 4. The bond angles are 109.5 o. A tetrahedral geometry has.

Compound molecular geometry table kowerncure
The valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model focuses on the bonding and nonbonding electron pairs present in the outermost (valence) shell of an atom that connects with two or more other atoms. 2 Linear electron geometry Molecular Geometries VSEPR geometries VSEPR table of molecular geometries

amppinterest in action Molecular geometry, Molecular, Study tools
Explore molecule shapes by building molecules in 3D! How does molecule shape change with different numbers of bonds and electron pairs? Find out by adding single, double or triple bonds and lone pairs to the central atom. Then, compare the model to real molecules!
Untitled Document
Figure 8.6.1 8.6. 1 shows the various molecular geometries for the five VESPR electronic geometries with 2 to 6 electron domains. When there are no lone pairs the molecular geometry is the electron (VESPR) geometry. When there are lone pairs, you need to look at the structure and recognize the names and bond angles.

VSEPR Theory Geometry of Organic Molecules Chemistry Steps
The bond angle for water is 104.5°. Valence shell electron pair repulsion ( VSEPR) theory ( / ˈvɛspər, vəˈsɛpər / VESP-ər, [1] : 410 və-SEP-ər [2] ), is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. [3] It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm.

Electron Geometry VS Molecular Geometry Difference between Electron
Chapter 21 Index By the end of this section, you will be able to: Predict the structures of small molecules using valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory Explain the concepts of polar covalent bonds and molecular polarity Assess the polarity of a molecule based on its bonding and structure

Pin by Siphora Ketchakeu on organic chemistry 1 Teaching chemistry
1. Linear: It refers to the geometry shaped by a central atom surrounded by two other atoms. The atoms are arranged in a straight line, and the angle between the bonds is 180 °. The VSEPR notation. Examples of molecules with linear geometry are carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), beryllium chloride (BeCl 2 ), and nitric oxide (NO). 2.
Pin by ryan britt on school Molecular geometry, Chemistry classroom
Molecular geometry gives information about the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.

Pin on IB Chemistry
Home Bookshelves General Chemistry Map: General Chemistry: Principles, Patterns, and Applications (Averill) 9: Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models

moleculargeometrychartmoleculargeometrychart22012653 MOLECULAR
VSEPR Theory is short for Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory, a method of organizing molecules based on their geometric structures. In chemistry, VSEPR Theory is based on the principle that each atom in a molecule will seek a geometry that maximizes the distance between valence electron pairs, thus minimizing electron-electron.

Download Molecular Geometry Chart for Free FormTemplate
Ketzbook explains molecular geometry, VSEPR theory, and the 5 basic shapes of molecules with examples for each one.For a limited time, earn double FREE stock.

Chem College Electron Geometry and Steric Number Scientific Tutor
1. Linear: It specifies the geometry shaped by a central atom surrounded by two other atoms. The atoms are arranged in a straight line, and the angle between the bonds, or bond angle, is 180 °. The VSEPR notation is AX 2. Examples of molecules with linear geometry are carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), beryllium chloride (BeCl 2 ), and nitric oxide (NO). 2.

Different Shapes CHEMISTRY COMMUNITY
Basic Molecular Geometries (or Shapes) where the Central Atom has No Lone Pairs Consider a molecule composed of only two types of atoms, A and B: A=central atom B=outer atoms For three or more atoms in a molecule, general formula: AB# (where #=2-6) 3 of outer atoms are at equatorial positions, 120° from each other

Electron and Molecular Geometries Chemistry Chemistry, Molecular
Molecular Geometries The VSEPR theory describes five main shapes of simple molecules: linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Apply the VSEPR model to determine the geometry of molecules where the central atom contains one or more lone pairs of electrons. KEY TAKEAWAYS Key Points